Understanding Pneumonia in the Elderly
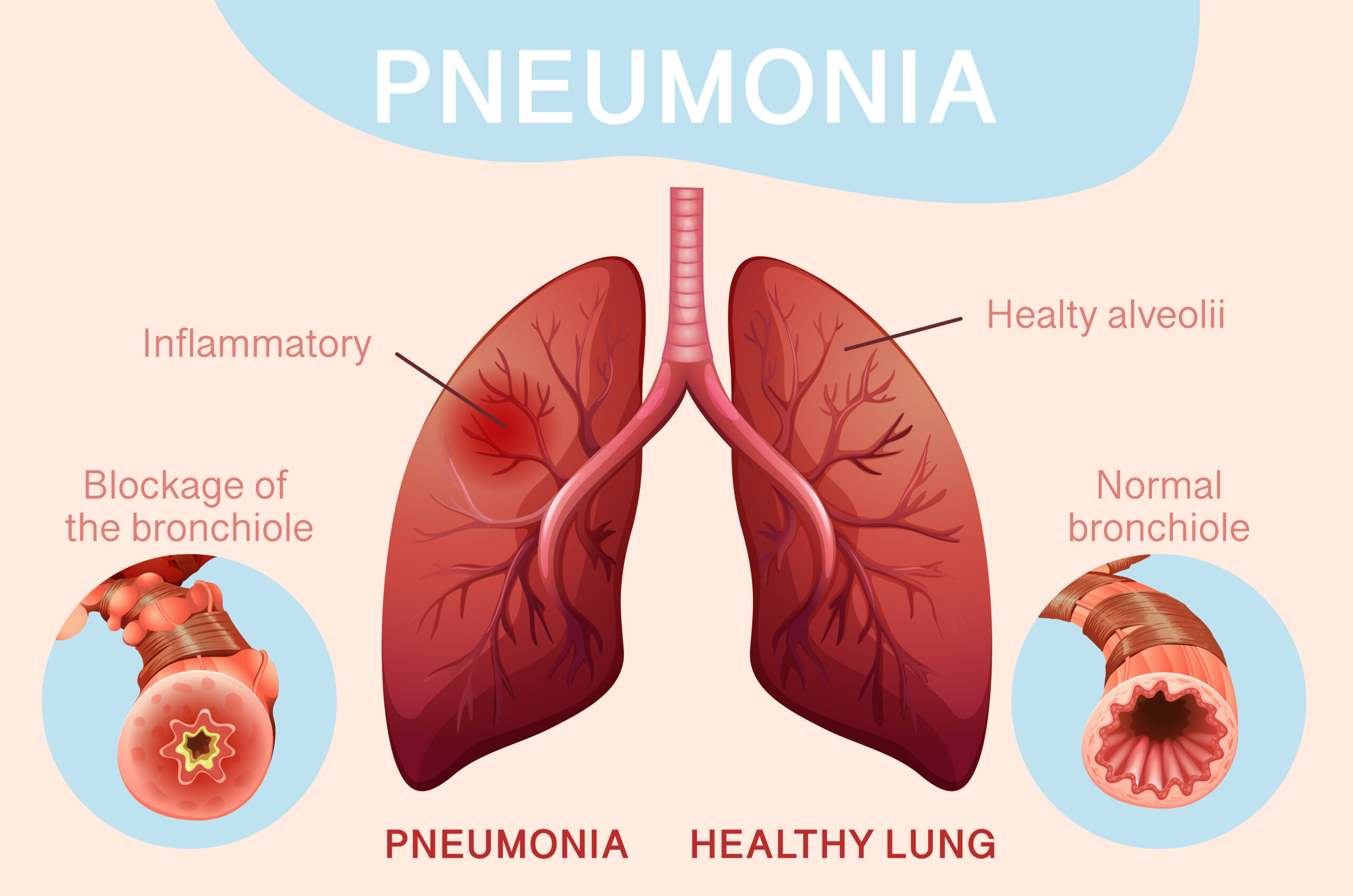
What causes pneumonia in elderly? This serious lung infection inflames the tiny air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs, leading to symptoms such as cough and shortness of breath. While pneumonia affects individuals of all ages, it is particularly deadly for the elderly, causing higher morbidity and mortality rates. Older pneumonia is often overlooked in discussions regarding respiratory health, yet it can severely impact older adults who have weakened immune systems and underlying conditions, making them more susceptible to complications. Unlike younger patients who might experience typical symptoms like chest pain and high fever, older individuals often present with confusion or sudden loss of mobility and may require hospitalization.
Causes of Pneumonia in the Elderly
When we spoke to Dr. Samir Garde, Director of the Dept of Pulmonology and Lung Transplant at Gleneagles Hospital, Parel, he explained that pneumonia in the elderly stems from various factors. These include weakened immune function due to aging, chronic health conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), diabetes, or heart disease, and lifestyle factors like poor nutrition or lack of physical activity, all contributing to weakened lung function and reduced recovery capacity.
Recognizing the Symptoms
The symptoms of pneumonia in the elderly include cough, fever and chills, chest pain, fatigue, shortness of breath, and rapid breathing. These symptoms can significantly impact daily activities and peace of mind. Elderly individuals should seek medical attention if they experience additional symptoms such as confusion, difficulty breathing, abnormal body temperature, and severe chest pain.
Diagnosis and Detection
Pneumonia in the elderly can be detected through blood tests, CT scans, and X-rays. Following a doctor’s instructions is essential to enhance the quality of life for those affected.
Comprehensive Treatment
The treatment for pneumonia should be all-inclusive, involving antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and supportive care, which includes hydration, monitoring oxygen levels, adequate rest, and pulmonary rehabilitation. Prompt treatment can prevent severe complications such as respiratory failure, lung abscess, sepsis, fluid accumulation in the lungs, and even death in elderly patients.
Prevention Tips for the Elderly
Preventing pneumonia in the elderly involves several key steps:
- Vaccination: Ensure to get pneumococcal and influenza vaccines.
- Hygiene: Regular hand washing and maintaining personal hygiene.
- Protective Measures: Wearing a mask and disinfecting frequently touched surfaces.
- Lifestyle: Avoid crowded places, quit smoking, eat a balanced diet, exercise daily, get sound sleep, and stay hydrated to keep the lungs healthy.